|
|
    |
 |
|
|

| My Address: | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Career Objective: | ||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||
| Skills: | ||||||||||||||||
• Language Skills: English, Turkish and German • Programming Skills: HTML, C++, Pascal, FORTRAN and Microprocessor Assembly Language |
||||||||||||||||
| UNIVERSITY EDUCATION: | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| WORK HISTORY: |
||||||||||||||||
Ümraniye, Istanbul, Turkey, 11/87-04/89 (Nortel Networks Netaş Telekomünikasyon A.Ş.) To visit the Web site, please click here. |
||||||||||||||||
| Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) | ||||||||||||||||
Merrimack, NH, 04/84-10/86 (merged with COMPAQ & HP)
 Adnan had returned to the United States from his Military duty in the Turkish ARMY and he accepted a position as a senior systems engineer at DEC in Merrimack, NH. While he was working there, Adnan met a junior engineer Mr. Richard Maynard, who had recently completed his studies at Worcester Polytechnic Institute. Adnan motivated him at DEC to work on embedded microprocessor based hardware and firmware. A fun project was the alteration of DEC's keyboard electronics to function with an Apple Computer's Macintosh. Adnan also worked with an HPIB instrumentation to automate testing of magnetic recording heads using a computer and a spectrum analyzer. For a short time, he participated in the PANTHER computer voice-data project group and also, he started on a Q-Bus modem board architecture design using Rockwell chips. During these projects, he discovered the need for a dual-port RAM (DPRAM). In the meantime, Adnan became a Naturalized Citizen of the United States in 1985 at the historic Faneuil Hall in Boston, Massachusetts. |
||||||||||||||||
| International Cospas-Sarsat Programme with Proteon, Inc. | ||||||||||||||||
Waltham, MA, 06/82-04/84
 The four founding countries led development of the 406 MHz marine EPIRB (Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon) and ELT (Emergency Locator Transmitter) in 1982. As an integral part of worldwide search and rescue, the Search And Rescue Satellite Aided Tracking (SARSAT) System is operated to detect and locate mariners, aviators, and recreational enthusiasts in distress almost anywhere in the world at anytime and in almost any condition. The SARSAT system uses satellites in low-earth and geostationary orbits. The satellites relay distress signals from emergency beacons to a network of ground stations and ultimately to the U.S. Mission Control Center (USMCC) in Suitland, Maryland. The EPIRB signal would be transmitted from the location of the distress with a Radio Frequency Signal 406 MHz PSK (Phase Shift Key). The data communications are Manchester encoded and the signal has a duration of 0.5 seconds. The signal would then be re-transmitted every 50 seconds. The emergency beacon's message is either a 112-bit "short" message or a 144-bit "long" message, both including 49 bits of identification plus position information. The data has a training sequence and a frame. For error-control coding the BCH Code is used. Adnan developed Real-time firmware for an embedded CMOS Intel 8051 microprocessor and he designed digital and analog circuits for the wireless receiver. Adnan also defined the user interface for the hand-held receiver with a small LCD display, switches and audio-visual indicators. Adnan's work entailed extensive coding using assembly language programming, debugging, lab testing and in-circuit-emulation for the firmware. And he designed a handheld verification receiver, which would test the emergency code transmitted by ships or airplanes in an accident. They would transmit emergency beacon, and you would verify that with his handheld signal verification device; it operated on batteries. An initial prototype was built and soon thereafter, the manufacturing of these verification receivers began. When Adnan was finished with his project, his boss said that it was a complete success in France. Upon the successful completion of this project his position at Proteon, Inc. was phased off and he journeyed back to TURKEY to serve in the ARMY's Infantry. Later, this Company moved in the direction of Local Area Networks (LAN). To visit the Web site of SARSAT, please click here.  |
||||||||||||||||
| Racal-Vadic, Inc. | ||||||||||||||||
Sunnyvale, CA, 06/80-05/82
  In the year 1981, Adnan also motivated one of his classmates from High School to work with modems too. His name is Vedat Eyüboğlu, who was at that time a Ph.D. candidate at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. Vedat had before completed his undergraduate studies in electrical engineering at Boğaziçi University in Istanbul, Turkey. Adnan helped him to find a job with modem-technology at Codex Corporation. After Adnan had suddenly lost his job, he left the Silicon Valley California with a Volkswagen automobile. He first drove east to New York and then north to Boston, where Adnan interviewed with ZOOM Telephonics, Inc.. He became a technical start-up advisor to ZOOM™ by pointing a new direction for this Company in modem(s) and data communications field. Adnan's talks encouraged and motivated the top two executives at ZOOM™, Frank Manning and Peter Kramer, by pointing a new direction for their Company. Frank Manning had earned his Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Adnan's first task was to start up a new modem company in Boston to compete with the British Racal-Milgo and Racal-Vadic in California. Finally, that was the only outcome after a long and difficult journey across the United States, from San Francisco to Boston with a Volkswagen automobile (1982). A few years later, Adnan was invited to a simple diner and he was served a bowl of bean soup for his efforts. But Adnan did not join this Company in Boston. Instead he accepted a position at Proteon, Inc., where Adnan worked on a project for Search And Rescue Satellite Aided Tracking (SARSAT). ZOOM™ was just another small start-up company in Boston manufacturing speed-dialers for telephones. Today in 2009-2010, a Fortune 500 company manufacturing modems and other data communications products for the global market. Racal Electronics plc was once the third-largest British electronics firm. |
||||||||||||||||
| NCR Corporation | ||||||||||||||||
Ithaca, N.Y., 05/79-06/80 (merged with Axiohm IPB, Inc.)
 |
||||||||||||||||
| Cornell University & Westchester Community College | ||||||||||||||||
Ithaca, N.Y., 09/78-05/79 & Valhalla, N.Y., 09/73-05/76
  A long time ago when he was still a student at Cornell University, a network called "ARPANET" was developed by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in the United States of America. When plans proceeded in 1978 to expand this network globally and internationally, a new name, "inter-net", was created by Adnan Tuncel on the CORNELL University Campus. He then used the term "client-server architecture" to describe how the internet would work. To visit CORNELL Universities School of Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE), please click here.  |
||||||||||||||||
| |
||||||||||||||||

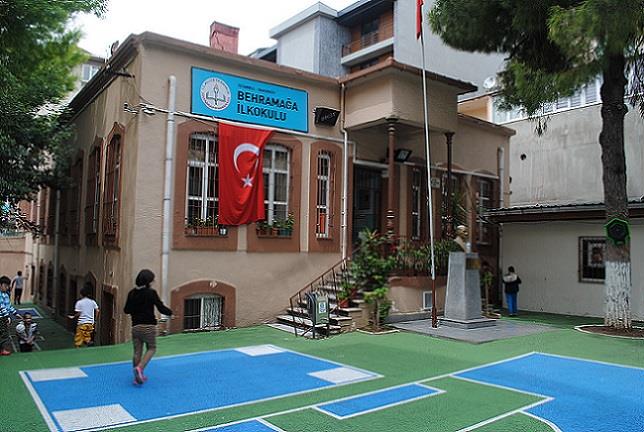
Mr. Douglas C. EngelbartMr. Douglas C. Engelbart was the father of the computer's mouse in the 1960s at Stanford Research Institute. In the year 1967, he patented his new invention (Patent-number: 3.541.541), but from where did he get this idea, that a personal computer could have a mouse? Who first conceived of the idea???Mr. Engelbart got this idea in 1960 from a six year old first grade elementary school student; indeed, student-number 172 Adnan Tuncel, at his Elementary School in İstanbul, Bakırköy Behram Ağa İlkokulu. After Adnan had seen for the first time a computer monitor in a classroom at his Elementary School, he explained in all detail that a computer's mouse could be made with a small rubber ball inside it, in order to move an arrow cursor as the X-Y position indicator on the display system and to click. Adnan was describing a new concept in personal computing and he was only a six year old child at the time. When asked what would one use this computer's mouse for, Adnan replied: "Facebook" and he also indicated that it would be the means for friendship and to keep in touch with classmates at his elementary school. Finally in 1983, a personal computer was introduced with a mouse for the first time by Apple Computers in Silicon Valley, California. It was an important year for country and mankind, but many years later as the technology advanced, the small rubber ball inside the computer's mouse was replaced with laser technology. Adnan also believed that he was the first human being who "double-clicked" for the first time the mouse of a PC in a laboratory for country and mankind. This important moment was never recorded but it happened during this project at the PROTEON Company, where Adnan was working as an electrical engineer (1982-1984). He stumbled upon double-click when his project had a few push-button switches. At first, he was trying to do something else. Indeed, he wanted to eliminate the effect of a push-button switch from bouncing twice when he pressed, so that one would not do something twice accidentally. Inside this small problem was a large problem struggling to get out. After he had this problem solved, Adnan said: "Success is often the result of taking a misstep in the right direction." Thus, he concluded that there were three logical states instead of two in the state diagram of a single push-button switch. Adnan even wrote a two page lab report about the multiple uses of the mouse, describing: 1. Double-click ("Open Sesame" function) 2. Press & Pull (Scoop function) In this special lab report he showed a way how to write software for all personal computers with a mouse. He used the word "Windows®" to describe a new Operating System (OS). Adnan further explained that at the top of the computers screen these four OS commands would always be displayed: File, Edit, View, Help. The windows would open (appear) and close (disappear) with menus inside the windows to operate a personal computer. The arrow cursor would then be used to scroll and select OS commands from the menu. Any item on the menu, which is pointed by the arrow cursor would be marked (reverse imaged) to indicate that a selection is being made. After the selection process, the window would close and the computer's screen would return to normal. In conclusion, he wrote a comment: "I would found a company named Micro-soft™ to write software for all the microcomputers in the world." "A subtle thought that is in error may yet give rise to fruitful inquiry that can establish truths of great value." But later he forgot all about his thoughts and ideas while serving in the ARMY's Infantry in TURKEY (1983-84). Today, Microsoft is the World's biggest Software Company. To visit Microsoft's Web site, please click here.  |
||||||||||||||||
| Military Service: | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Memories of Many Inventions and Ideas: | ||||||||||||||||
 
As a kid, his favorite hobby was to design the unique patches for many soccer balls. As he was learning one day the basic geometrical shapes when he was in third grade Elementary School, Adnan discovered that the design of a soccer ball is made up by interconnecting hexagons and pentagons. When Adnan was still in Elementary School, he had some creative ideas for construction techniques, he designed a new concept in construction cranes and he also drew architecture in High-School. When Adnan was still in the third grade Elementary School, he was very proud to design the interior architecture of the new Turkish Parliament TBMM in Ankara, Turkey. Adnan had also invented a food and he called it "Pizza" and then, he came up with the idea of a pizza cutter, which would be a round wheel-type slicer with a handle. (see below)  A photograph of his sister was etched on a metal surface by exposing it with the negative-film to intense light (i.e. photon bombardment), and someone as an adult had explained to him how a transistor in an electron tube worked. Adnan who was five-year-old at that time, was looking at the etched photo of his sister and argued, that "electron bombardment" could be used to etch the electronic circuits on a special materials surface. When asked what this material should be, Adnan replied: "Coal???" But his idea has led to the discovery, that this material was-indeed-Silicon. Some of Adnan's other ideas were as follows:
• Q-tips or cotton swabs. • Filter tipped cigarettes. • Earbud headphones. • Adjustable hats. • Front-load washing machines. • Eggs from caged hens. • Concrete pump. • Cement mixer truck. • Stealth aircraft. • Bulbous bow for ships. • Fast trains. • Cell phone. • Shopping mall. • Inflation of money in Turkey. • Single European currency. • Japanese conveyor belt sushi restaurants. • Daylight Savings Time. (The clocks are turned forward / back one hour.) Adnan expressed most of his ideas by drawing.
In the year 1960, when he was playing in the schoolyard with a handmade flying toy as a kid, he conceived of the idea for a new invention: a flying vehicle, which would take off vertically and then it could fly further horizontally. Afterwards, it would also land on some place vertically. He began sketching his flying vehicle to describe it perfectly to others in broad outline, but he did not know what to name this flying vehicle. One day his Math and Physics Teacher Mr. Diethelm Buttkus at Istanbul German Lyceum had explained to Adnan what the greek word "heli" meant: "winding, spiral". Adnan remembered right away his flying toy as a kid. Later, he gathered a few of his classmates around him at his High School and he created a name for his flying vehicle: "Helicopter". Adnan had some design ideas for ships and intercity busses as well and he then began sketching his new concept of these modern busses. Also in 1960, Adnan first conceived of the idea to design and build modern airplane turbine engines in a cylinder instead of propellers. He then described these air-engines exactly by sketching as they would be used by modern airplane companies such as Boeing and Airbus. He also drew modern fighter jets for the Air Force and new tanks for the Army. Adnan was never idle as a seven year old student at his elementary school. |
||||||||||||||||
| N A S C A R : | ||||||||||||||||
 When Adnan Tuncel was six years old, he proposed the construction of a major oil pipeline to carry petroleum from Baku, Azerbaijan to Ceyhan, Turkey on the coast of Mediterranean Sea. Adnan was simply against the idea of oil-tankers and other ships carrying petroleum through the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles in Turkey. The project of this 1,099 miles long Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline got a head start by the Presidents of Turkey, Georgia and Azerbaijan in the year 2002 and when it was finished in the year 2006, crude oil started to flow from Azerbaijan to the coastal city of Ceyhan on the Mediterranean. Today, the Country of Azerbaijan earns about 30 billion dollars annually from this Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan oil pipeline. To see the route of this oil pipeline on the map, please click here. And in 1970, during a Geography Class at İstanbul German Lyceum, Adnan proposed to build a dam on the river Euphrates. The dam would be built both to generate electricity and to irrigate the plains in the region. Arable land in the plains in upper Mesopotamia would be irrigated via gravity-flow with water diverted from the dam through the tunnel system. The dam and the tunnel system were two major components of the project. It was also Adnan's Idea in High School to build many containers for international trade. These containers would then be transported by ships, trains (railway) and/or trucks. When his teacher, Klaus Stolzenberg, had asked Adnan: "How would you put these containers from ships onto railroad cars or trucks?", Adnan replied: "With cranes." At a later time, Mr. Stolzenberg had asked Adnan to create a new name for an airplane company, but he had also requested that this name will start with the letter "A". Therefore after some careful thought, Adnan had created the name "AIRBUS" for this Company to build airplanes in Europe. |
||||||||||||||||
| Visa and MasterCard: | ||||||||||||||||
These magnetic swipe cards, which are currently being used as ATM cards or debit cards etc., were an idea of ADNAN TUNCEL when he was seven years old (1961). At the time of his invention, Adnan thought that the people could spend the money in their bank account electronically with the use of computer technology. Adnan had also thought, that the package-delivery requirements of the future could not all be handled by a postal service alone. Therefore, Adnan strongly recommended the establishment of two private delivery Companies, which he named: Federal Express (Fed Ex) and United Parcel Service (UPS). After he had drawn the Logos for each of these Companies, he chose the colors for their delivery trucks as white and brown.
In an algebra and geometry class at his High School (İstanbul German Lyceum), he came up with the idea of a mechanical billboard to display three different advertisements instead of just one by alternating and periodically changing the display from one ad to another. He also derived an equation to maximize the volume inside the mailboxes for the apartment buildings. Many years later, during a final exam, when he was a senior student at the Cornell University studying Electrical Engineering in 1978, he discovered Manchester Encoding, without knowing that it had been already discovered in England at Manchester University, (According to Wikipedia). As he was describing his discovery during the final exam, Adnan noted that whenever the bits in sequence changed from 1 → 0 or 0 → 1, then a skip occurred, therefor watchdog action was required. (Manchester code was first used in serial data communications.) One of his friends at Cornell University, Erhan Kudeki, consulted Adnan about dish antennas for DirecTV. In high school (the German Lyceum in Istanbul), Adnan envisioned such products: door, house and telecommunications, video monitoring for the SSS Siedle Company in Germany. He drew the emblem for the Technical University of Munich (TUM) in 1969.  After drawing the above "TUM" Logo, Adnan created the following zip code for Heidelberg, Germany: 69117. When Adnan was still a young child, he also created many names for the American, European and Japanese corporations and designed many logos for them. These following Names and their Symbols or Logos were created by Adnan Tuncel:       |
||||||||||||||||
| BACKGROUND: | ||||||||||||||||
He was on Dean's List. Vice President and President of Turkish Students Association at CORNELL (1977-79). Enjoys outdoors and hiking. Dual citizenship of both U.S.A. and TURKEY. Adnan travels like Marco Polo. |
||||||||||||||||
| LIST OF SCHOOLS: | ||||||||||||||||
   
   
|
||||||||||||||||
| *.*.*.* Adnan Tuncel *.*.*.* | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
   
|
||||||||||||||||
| THE END | ||||||||||||||||
 111 Yale Ave. N Apt. 309
111 Yale Ave. N Apt. 309